ECOLEAF: INTRODUCTION TO RENEWABLE ENERGY


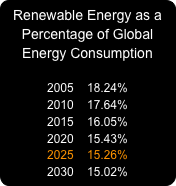
The challenges of today are greater than they ever have been: increasing energy use coupled with a growing population means that the global need for energy will double over the next 25 years. Although the rate of renewable energy will also increase during this time, it will not increase fast enough to keep pace or even to have a substantial impact on worldwide energy consumption. At the current rate at which renewable energy is being adopted, the global net effect will be a mere decrease of three percent over the next 25 years. For renewable energy to achieve any significant impact, new methods of innovation need to be devised, developed, and implemented.
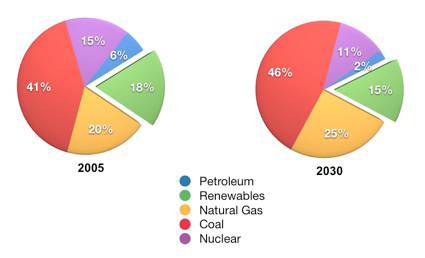
Graph: U.S. Energy Consumption in 2005 and 2030
OUR CURRENT REALITY
1)Electricity production is our primary polluter in terms of carbon and greenhouse gas emissions. Coal power plants and natural gas power plants are the key players, but all of us are to blame: every day and every time we use computers, lights, refrigerators—any appliance or item requiring electricity—we are exacerbating the problem.
2)For the past 100 years, the U.S. has been the leading global polluter/producer of greenhouse gas emissions. Great minds such as Tesla (who created AC power) and Edison (who created DC power) gave us the ability to lead the way in energy-distribution systems and technologies. Unfortunately, however, we still lack the ability to create new systems that can compete with and displace the burning of fossil fuels to generate electricity. Renewable technologies remain cost-prohibitive technologies.
3)Worldwide electrical energy use will double over the next 30 years. The U.S. will still be a large producer of greenhouse gases, but the problem will get out of control due to increasing power demands coming from the remainder of the globe. The technologies, innovations, and power plants the U.S. has engineered—plants that create viable energy and continuous pollution—will be replicated throughout the world. That’s not a good thing.
4)In 2009, China overtook the U.S. as the top producer of greenhouse gas emissions, yet China still claims to be a developing nation. China and the rest of the world will continue to follow the U.S. example…which means that all of us are speeding towards a climate carbon crisis.
UNDERSTANDING ENERGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
Mother Nature is sick. Man-made pollution and global warming are making her worse. If the status quo of “do nothing” continues to hold sway, greenhouse gas emissions will continue to rise, thereby forcing climate change. The U.S. produces 22% of the world’s greenhouse gases. The primary culprit is the generation of electricity, followed by pollutants produced by transportation. Currently, the U.S. has no feasible means of significantly reducing outputs; unfortunately, the rest of the world is following suit by installing new (polluting) power plants. Further exacerbating the problem, China out-produced the U.S. in carbon dioxide emissions in 2009. Moreover, not only will China continue to out-produce the U.S. in carbon emissions, their emissions will be 41% higher than the U.S. by 2030.


INTRODUCTION



Stay Informed
Get updates and action alerts.


next
Delivering Green Clarity in a Carbon-Troubled World™
Copyright © 2008 - 2010 by ECOLEAF™. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.